UNIT 2: PARALLEL AND PERPENDICULAR LINES, SET SQUARE RULERS.
DEFINITIONS:
PARALLEL LINES are lines that never join or meet.
PERPENDICULAR LINES are lines that join or meet making 90º angles (right angles)
SET SQUARE RULERS
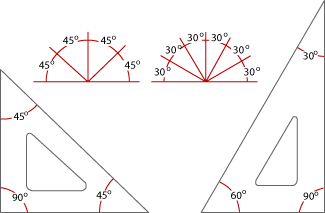
45º Set Square Ruler (Escuadra) 60º-30º Set Square Ruler (Cartabón)
How do we use the set square?
You have to handle your set square softly and with accuracy without
exercising too much pressure on them, only the needed one to avoid
movement.
PARALLEL LINES are lines that never join.
HOW TO DRAW PARALLEL LINES
- The 45 set square hypotenuse (longest side) is placed attached to the line to which we want to draw the parallels (GUIDE).
- The 60-30 set square hypotenuse is attached to the 45 set square leg.
- Fix the 60-30 set square and move the 45 set square upwards or downwards drawing the desired parallel lines along its hypotenuse.
PERPENDICULAR LINES are lines that join making 90º angles (right angles)
HOW TO DRAW PERPENDICULAR LINES
If we want to draw perpendicular lines to one direction, we will have to follow the first two steps as stated for parallel lines and then the following ones:
- Having fixed the 60-30 set square, the 45 set square is turned until the other leg is attached to the hypotenuse of the 60-30 set square.
- Draw the perpendicular line along the hypotenuse of the 45 set square.